We’ll reassure you right away! Fermenting vegetables with salt, also known as lacto-fermentation, is completely safe. There are no dangers associated with fermented vegetables.
Many people are afraid to start fermenting vegetables for fear of food poisoning. However, lacto-fermentation is a simple way of preserving vegetables without the risk of poisoning.
We are not the only ones to say so! The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and numerous studies recognize lacto-fermentation as a safe way to protect food from spoilage (ref.)

As a matter of fact, due to their natural acidity, lacto-fermentations are safer than raw vegetables and less dangerous than canning (ref.).
In addition, vegetable lacto-fermentation requires minimal equipment and has many benefits. No wonder fermented vegetables are prepared all over the world!
Go straight to the section that interests you:
- Why are fermented vegetables safe?
- Pathogens and fermented vegetables
- Fermented vegetables and botulism
- How to ferment safely?
Why Are Fermented Vegetables Safe?
Vegetable fermentation (lacto-fermentation) has been used throughout the ages. Before refrigeration, it was one of the most common techniques used to preserve vegetables and their nutrients.
The process is simple. You put the vegetables with salt in an oxygen-free jar. This creates an environment where only the good lactic acid bacteria can grow.
To defend themselves against other microorganisms, the bacteria create lactic acid, which makes the environment acidic and inhospitable to pathogens.
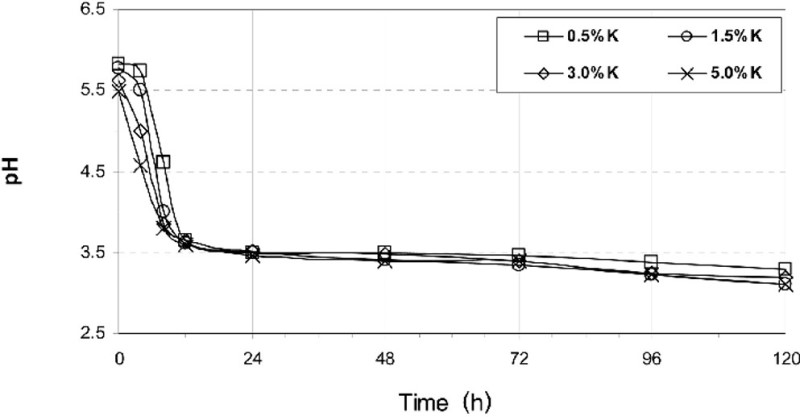
pH evolution of kimchi recipes according to fermentation time (ref.)
In just a few hours, the acidity of fermented vegetables drops to a safe level.
In fact, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), canned or fermented foods should have a pH of less than 4.6. Below this level of acidity, pathogenic bacteria cannot grow (ref.)
Fermented vegetables quickly reach this threshold and are therefore very safe!
In summary, during lacto-fermentation, the vegetables are in an environment that is:
- Without oxygen
- Salty
- Acidic
- Full of good bacteria
This environment prevents any pathogenic microorganisms from taking hold and spoiling the vegetables.
Lacto-fermented vegetables can then be stored for several years without any problem.
Furthermore, it is very easy to identify a successful fermentation from a failed one. So there is no risk of inadvertently poisoning yourself.
Is There a Risk of Pathogens From Fermentation?
Fermenting vegetables has been shown to significantly reduce pathogenic bacteria (salmonella, E. coli, listeria…) found on vegetables.
Studies have observed an almost total elimination of various pathogens in fermenting kimchi in less than 5 days (ref.):
- Salmonella typhimurium
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Clostridium perfringens
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- E. coli.
Lactic acid bacteria produce a large amount of very powerful organic acids and compete with other pathogens.
It’s like raising a fearsome army to defend our vegetables!
So fermented vegetables are simply safer than raw vegetables. And yet, raw vegetables are already among the safest foods!
Obviously, you have to apply basic safety guidelines and choose healthy vegetables, just as you would when cooking.
Several governmental organizations also recommend using lactic acid bacteria strains to guide (ensure) the fermentation process.
Can You Get Botulism From Fermented Vegetables?
Unlike canning or oil marinades, there is no risk of botulism in fermented vegetables!
Some cases of botulism in fermented vegetables have been reported in Thailand, but in these cases the fermentation process was faulty. It was either not using salt, not enough salt, or was made without the lactic acid bacteria (ref.).
Botulism is a serious disease caused by a bacterium (Clostridium botulinum) found in the soil.
When this bacterium is found in an oxygen-free, low-acid environment, such as in a poorly sterilized can, it creates a dangerous toxin.
In vegetable fermentation, lactic acid bacteria create an acidic environment within a few hours that quickly kills the Clostridium botulinum bacteria.
In an acidic, salty environment full of other microorganisms, the bacteria that cause botulism cannot create toxins.
Fermented vegetables do not need to be sterilized during preparation.
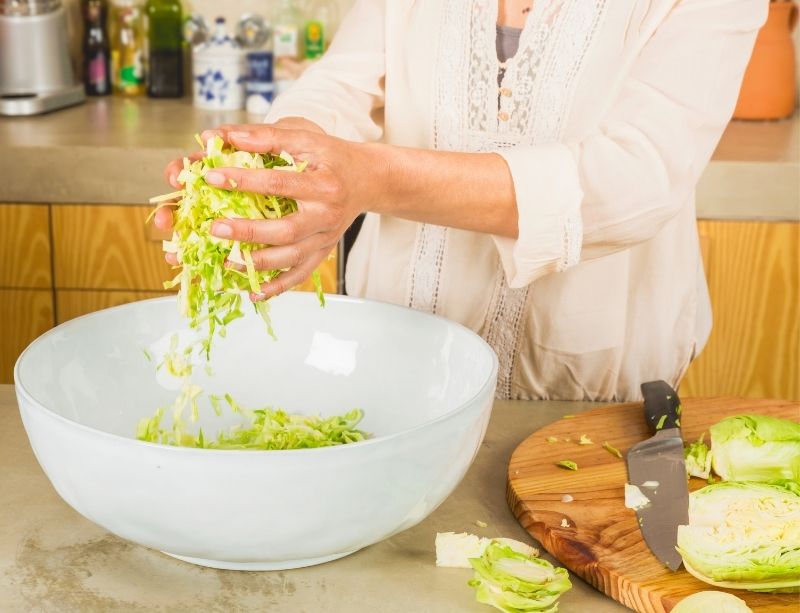

How to Safely Make Fermented Vegetables?
When making sauerkraut (or any vegetable fermentation recipe), you don’t need to take any more precautions than you would when making a salad!
Just make sure to:
- Use clean equipment
- Wash your hands before touching the food
- Have healthy, fresh vegetables
- Follow the basic principles of lacto-fermentation (add salt, and use vegetable that naturally have good bacteria, or add good bacteria)
And that’s it! The lactic fermentation process takes care of everything to keep your vegetables safe.
Not sure about your fermenting jar? Check out Lacto-Fermentation Problems Troubleshooting (FAQ) to differentiate between a safe fermentation and one that didn’t work.
Fermenting vegetables is simple and safe to prepare at home. Just follow the basic principles of fermentation, our 5 tips for successful fermentations, or simply follow one of our fermented vegetable recipes.

