You want to preserve your fruit and vegetables, but you are not sure whether to can or to ferment them? No worries! Here you will learn the main differences between these two food preservation techniques. Harvest season is just around the corner!
Although they are quite different, both pickling (canning) and fermentation allow you to preserve food safely over time. Each method has its advantages and strengths.
Go directly to the section that interests you:
How to Preserve Fruit and Vegetables?
Preserving food means preserving its properties (taste, nutrients, etc.) by protecting it from natural decay.
Fermentation and canning are both accessible and easy to do at home.
Although they work differently, they both help to preserve fruit and vegetables safely.
Regardless of whether you can or ferment, preserving fruit and vegetables has many benefits:
- Being able to eat locally all year round
- Extending the harvest season
- Saving money by buying large quantities of seasonal fruit and vegetables
- Harnessing the full flavour of fruit and vegetables

How Does Canning Work?
Canning is the process of sterilizing food through heat.
This is done by placing the food in glass jars which are then treated with boiling water. The heat will kill microorganisms, creating a sterile environment. This allows fruit and vegetables to be stored at room temperature.
For acidic foods, such as fruit and pickles, a large pot of boiling water can be used to sterilize the food.
However, for low-acid vegetables or fruit, an autoclave should definitely be used to sterilize at temperatures above 116°C (240°F). Meat, fish, etc. can also be canned in an autoclave.
The heat processing time varies according to the size of the jars, the type of food, and the altitude. When canning, always refer to reliable sources that provide clear sterilization times.
How Does Lacto-Fermentation Work?
Lacto-fermentation preserves food through natural acidity, the absence of oxygen, the presence of salt, and healthy organisms (probiotics).
The acidity alone is sufficient to ensure that the food is safe to eat, as pathogenic microorganisms (botulism, salmonella, etc.) do not survive in an acidic environment.
In addition, lacto-fermentation offers a set of characteristics that preserve and even increase the quality of food.
Unlike canning, lacto-fermentation does not destroy, it creates!
How does lacto-fermentation work?
- Adding salt to the recipe allows the good bacteria to grow.
- The bacteria produce lactic acid.
- The acidity protects against the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Salt and the absence of oxygen slow down food spoilage.
- Good bacteria increase the nutritional quality of food and protect it from invaders.
Are you a visual learner? Check out our infographic on lacto-fermentation to discover this process!
Is Pickling Fermentation?
No, pickling is not fermentation. Pickling use vinegar and heat to kill microorganisms. Fermentation, on the other hand, let the natural bacteria create lactic acid that will keep the bad microorganisms at bay, while improving the nutritional quality of the vegetables.
Comparing Pickling vs Fermentation
To help you find your way around, here is a table that summarises the differences between these two methods of preserving fruit and vegetables.
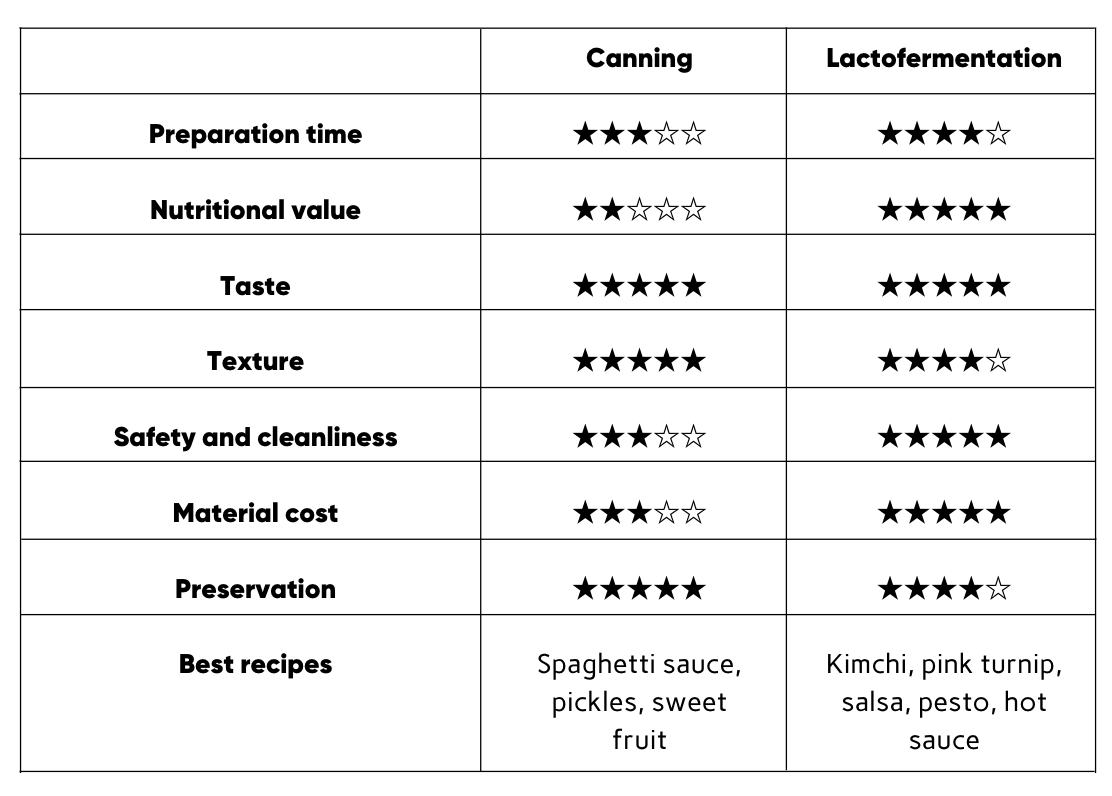
Which is Easier to Prepare?
Fermentation is easier to prepare than canning and involves fewer steps.
Canning involves a rigorous method and many steps to ensure food safety:
- Sterilizing the equipment
- Preparing food (cutting, acidification, cooking)
- Placing in jars
- Heat sterilization (from 10 minutes to several hours)
- Cooling
Lacto-fermentation is much simpler:
- Washing the equipment
- Preparing the food (cutting, adding salt)
- Placing in jars
Which Has More Nutritional Value?
Lacto-fermentation retains more of the nutritional value of food than canning.
Canning and lacto-fermentation do not have the same effect on nutrients and vitamins in fruit and vegetables.
With canning, nutrients and vitamins are reduced during the sterilization of the jars. Heat also kills microorganisms and bacteria (both harmful and good).
Lacto-fermentation improves the nutritional value of ingredients. Through the action of the beneficial microorganisms, the food becomes more digestible and richer in nutrients.

Which One Is Tastier?
Lacto-fermentation and canning have different impacts on flavours.
Canning preserves the taste of ingredients over time. For example, applesauce will taste almost the same when canned as when eaten.
If you use an autoclave, you can also preserve low-acid fruit and vegetables. It is, therefore, possible to preserve a wide variety of foods without affecting their taste.
Lacto-fermentation changes the taste of food over time. Flavours change throughout the fermentation process. A cabbage will not taste at all the same before and after it is fermented into sauerkraut!
Fermented foods are salty, sour, tend to have more nuance in the mouth, and become more refined over time.
In addition, lacto-fermentation consumes the sugar in the food. Lacto-fermented vegetables and fruit lose their sweetness but create new flavours and aromas during fermentation.
Which One Has the Best Texture?
Canning helps preserve the texture of food. However, it is also a matter of preference.
Canning preserves the texture of ingredients over the long term; vegetables stay crunchier. Ideal if you want crunchy pickles over several months! With lacto-fermentation, vegetables tend to soften over time.
However, for some recipes such as hot sauces, salsa, kimchi, or lacto-fermented garlic, this is not a problem; quite the contrary.
To better understand the phenomenon, see How to preserve vegetables with lacto-fermentation.

Which Is Safer?
There are more dangers in canning than in lacto-fermentation.
Canning can present some risks, especially when low-acid foods are canned. Botulism is an important issue when canning low-acid foods. Cooking temperatures and times must be carefully observed.
Canned foods contaminated with botulism show no visible or noticeable signs of contamination.
Lacto-fermentation is safe, as there is no risk of contamination by pathogenic organisms.
The acidity of the vegetables and the presence of good lactic acid bacteria safely protect the vegetables (read: Are there any dangers in lacto-fermentation?).
In addition, it is very easy to identify if a fermentation has worked or not. For more information, check out Lacto-fermentation problems (FAQ).
Which Preserves Food Better?
Both canning and fermentation provide very good preservation over time.
Canned foods can be stored at room temperature for more than a year, ensuring that flavours and textures remain consistent. Once opened, a can should be stored in the fridge.
With lacto-fermentation, flavours change over time. Some recipes are worth fermenting for only a few days (pickles), while others gain in flavour and benefit from being stored for many months (sauerkraut, garlic, etc.).
Once opened, a lacto-fermented product should be stored in the fridge.
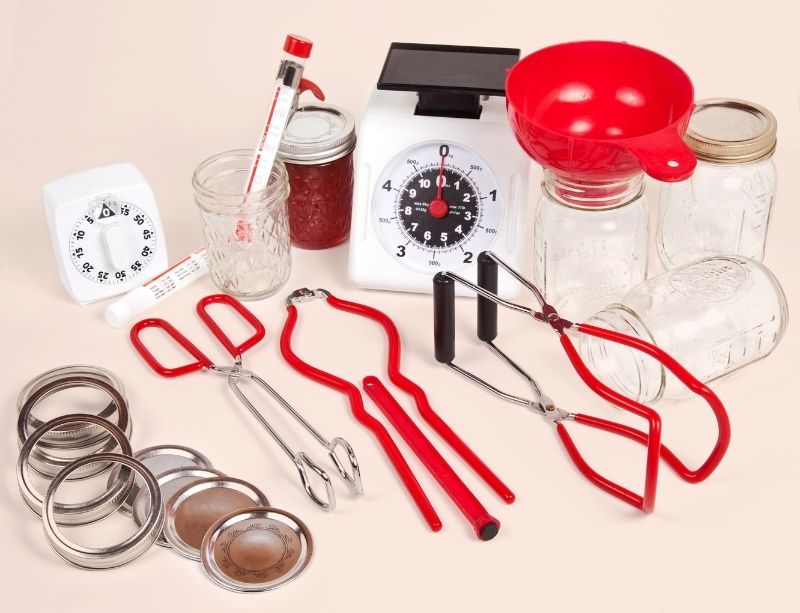

Which Requires the Least Amount of Equipment?
Lacto-fermentation requires less specialized equipment than canning.
The equipment required for canning and lacto-fermentation is typically different.
Canning requires several specialized pieces of equipment to be done safely:
- Jars and lids (new)
- Large pot or autoclave
- Jar rack
- Jar tongs
- Cooker (electricity)
Making lacto-fermentations requires very little equipment. You probably already have all you need to make your first recipes!
- Container
- Weight to keep vegetables submerged
Although there are all-in-one containers and specialized equipment, fermentation can easily be done with everyday equipment.
To learn about the different options available, see How to Choose Lacto-Fermentation Equipment.
Our Conclusion
What is best between canning and fermenting to preserve fruit and vegetables? Our answer: that depends on you!
Canning stands out for its ability to preserve the flavours and textures of vegetables over time. However, it requires more equipment and effort and destroys some nutrients.
Fermentation transforms fruit and vegetables into living foods, improves their nutritional value, and gives them new flavours. It requires little equipment and fewer preparation steps than canning.

